Accelerated Project Delivery Methods
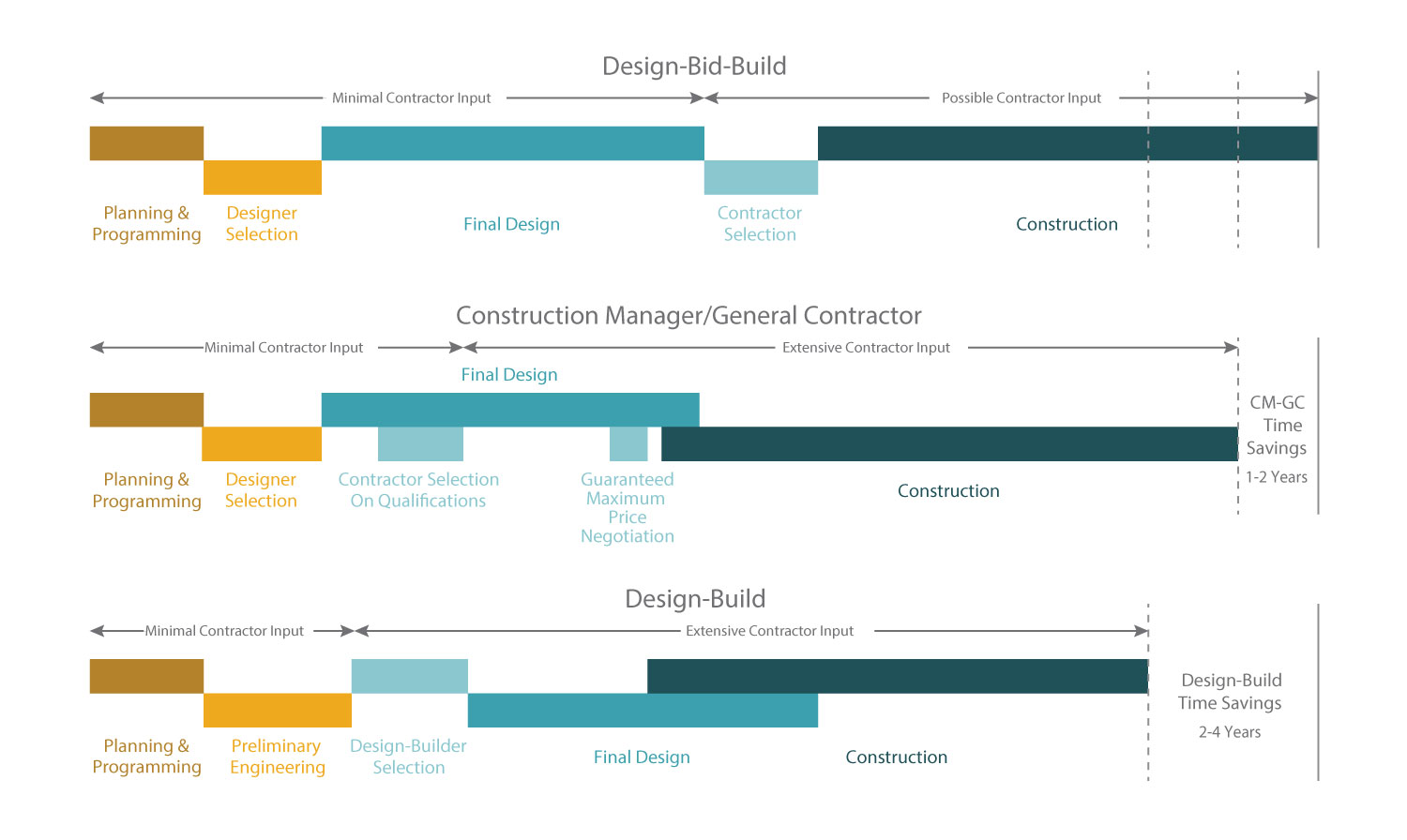
With the right contracting tools in place, NDOT can deliver roads projects faster than the estimated 7-12 years it takes to complete a major transportation project in Nebraska. Until now, NDOT was only authorized to use Design-Bid-Build, a contracting process which occurs sequentially. Now, in order to provide the earliest possible mobility, freight, safety and economic benefits to the public, NDOT can selectively use alternative contracting tools to help accelerate the largest and most complex road projects.
The Transportation Innovation Act authorizes NDOT to use the Construction Manager/General Contractor and the Design-Build methods for contracting. These two additional project delivery tools could save 2-4 years on project delivery time.
Accelerated Project Delivery Guidelines (PDF)
Accelerated Project Delivery Methods
- Build projects faster with the right tools
- Provide the earliest possible mobility, freight, safety and economic benefits to the public
- Does not replace Design-Bid-Build
- Used on the largest and most complex projects
- Committed to working with our Industry Partners
Construction Manager/General Contractor (CM/GC)
The CM/GC method involves hiring a construction manager at the beginning of the project where during design, the contractor provides the agency valuable time and cost-saving input regarding scheduling, pricing, phasing and constructability of the project. Streamlining the process and hiring a construction manager during the preliminary phase of the project accelerates project delivery.
Design-Build (DB)
The DB process allows the design engineer and contractor to be selected simultaneously, while also allowing for overlap between final design and construction activities. This results in accelerated project delivery because the traditional successive steps of Design-Bid-Build are condensed by managing contracts, final design, and construction concurrently with fewer steps.
Project Delivery Methods Schedule Comparison for Large and Complex Projects
Intended Use by NDOT
These alternative contracting methods are best suited for expediting the state’s most complex projects. They are not intended to replace the Design-Bid-Build process but instead, serve as additional “tools in the toolbox” to deliver large transportation projects more quickly to Nebraska citizens. Examples of possible projects using these expedited methods include completion of the Expressway System or other large complex capital improvement projects across the state. NDOT intends to carefully examine projects to determine the most appropriate project delivery tool to utilize. For the majority of projects, NDOT will continue to utilize our existing Design-Bid-Build method.
NDOT anticipates a two-step procurement process beginning with a short list of two to four teams that are selected based on qualifications. No design is required during this step. In step two, the short listed teams receive request for proposals (RFPs). The department will pay a stipend to qualified teams.
The criteria for evaluation of proposals shall include, but not be limited to, cost of the work, construction experience, design experience and resources available for the project (e.g. financial resources, manpower and equipment). The percentage of the evaluation criteria applied to any item shall be in the discretion of the department on a project-to-project basis, except that in all cases the cost of the work shall account for a minimum of 50 percent of the evaluation criteria. NDOT will work with industry partners as the criteria is developed.
Uses in Nebraska
In Nebraska, CM/GC and DB have been used for construction of public school facilities and municipal buildings.
These methods optimize taxpayer dollars by streamlining contracting steps. In addition, the end user realizes the benefit of the final product sooner than with traditional Design-Bid-Build.
Uses in Other States
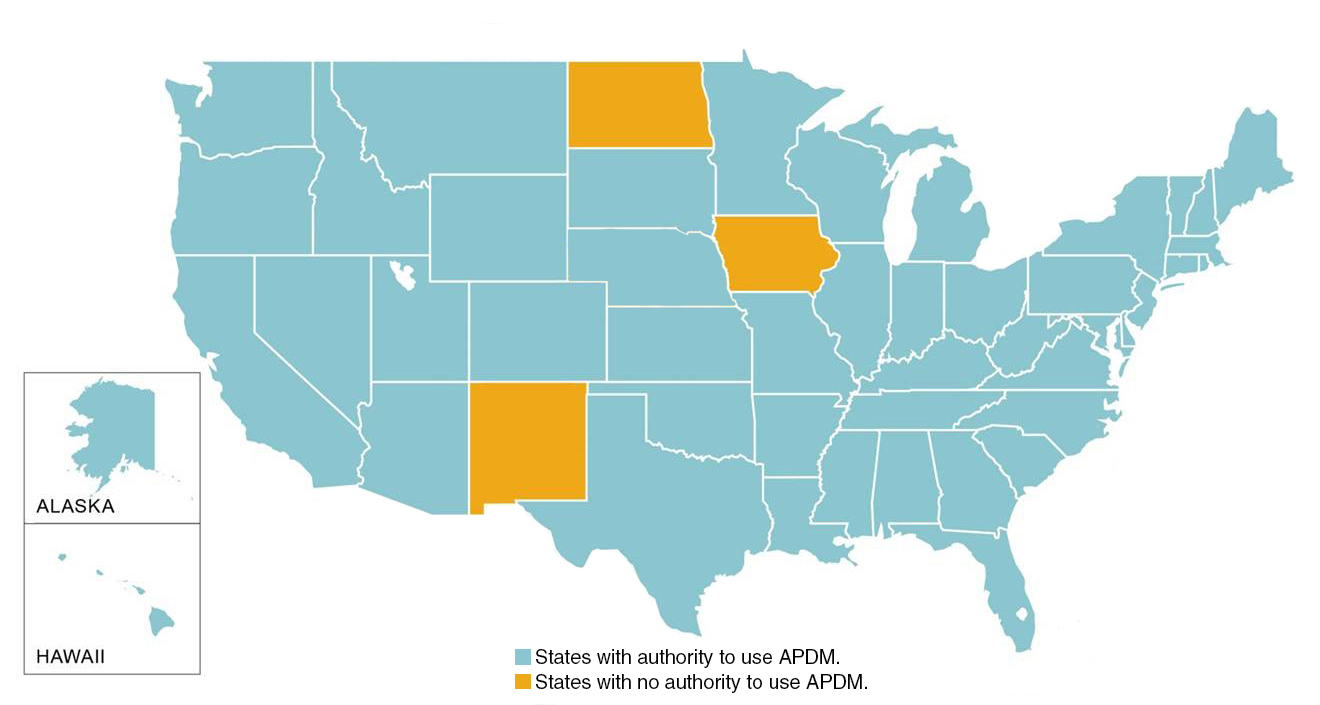
Over half of the United States utilizes some form of accelerated project delivery method with success. Currently, 47 states have the ability to use CM/GC and/or DB specifically for transportation-related projects. Examples include the transportation improvements on I-80 and I-15 in Salt Lake City in preparation for the 2002 Winter Olympics, as well as the Johnson County, Kansas Gateway project along the I-435, I-35 and K-10 interchanges.